This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Manufacturing Electronics at Home vs Outsourcing It to Other Countries: All You Need to Know

Andrey Solovev
Chief Technology Officer, PhD in Physics and Mathematics

Timur Yuldashev
IT Writer, PhD in Philological Sciences
- Preparing for Mass Production
- Domestic vs. Overseas Manufacturing
- Most Popular Countries for Outsourcing Electronics Production
- Asia
- North America
- East Europe
- What Companies Can Manufacture Electronics?
- Electronics Manufacturers
- Enclosure Manufacturers
- What is Minimum Order Quantity?
- Finishing Burst
- Product Assembly
- Testing & Certification
- Packaging
- Shipping Products
- Export/Import Customs Clearance
- Distribution
- Conclusion
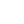
After completing the design of a new device, companies must find a factory for mass manufacturing. Today, outsourcing electronics production to other countries is a common practice. Companies that choose offshore factories can benefit from lower production or shipping costs, deeper expertise of local manufacturers, special export duties, political stability, and other factors. It is highly important to make the right choice from the very beginning because changing locations after the production launch can be quite costly. In this post, we will examine the world’s most popular locations for manufacturing electronics and talk about what you need to launch mass manufacturing.
Preparing for Mass Production
Creating an electronic product starts with development. This task can be completed in-house or outsourced to an electronics development company with expertise in a given field. Integra Sources specializes in developing IoT devices, power electronics, FPGA-based solutions, and other embedded systems for various industries. Contact our team to learn about our experience. After that, you should make sure your product is ready for mass production. Use the following checklist.
- Design for manufacturing and assembly
There is more than one way to make a properly functioning device. However, not all solutions are equally cost-efficient in terms of production. Simply put, the product must be designed in such a way that it is easy and cheap to produce. Professional electronics development companies design products with the manufacturing and technical capabilities of modern factories in mind, which is called ‘Design for Manufacturing and Assembly’.
- Product testing
Products under development undergo various tests at all phases of the process. The same goes for the final product. There are many types of tests designed for different devices. Read our blog post on PCB and electronics testing to learn more. Testing ensures the product meets the functional, non-functional, and certification requirements.
- Certification
Most electronic devices must be certified if you want to sell them. Certification proves that the product meets regulatory requirements and industry standards on safety, environmental protection, noise level, etc. Some certifications are mandatory, while others are voluntary. Learn more in our post on electronics certification in the U.S. and EU. Different countries impose different requirements on electronic devices, depending on their type and field of application. It’s important to obtain all the required certifications before launching mass production because altering the design will require changing the manufacturing process, which will lead to extra expenses.
- PCB design documents
These include the bill of materials (BoM) as well as the PCB schematic and layout. Our team uses Altium Designer and other CAD software for PCB design and layout. The projects created in such software can then be exported as Gerber files used for manufacturing. They describe copper layers, the coordinates of components, vias, and tracks on the board, and other details that factories need.
- Test software
Along with hardware, Integra Sources also develops embedded software for our devices. However, we strongly advise against handing it over to factories for the sake of IP protection. As a safety measure, we create test firmware that only checks if the board’s components are working properly but does not contain any business logic. The team can also develop software for test fixtures that automatically check the work of manufactured PCBAs in factories.
- Documents for enclosure design
These are the documents required to manufacture enclosures for the printed circuit board in a factory. They include a 3D model of the PCBA and assembly drawings if required. Although Integra Sources doesn’t design enclosures, we have reliable partners who can take care of this task.
If the product is tested and certified and you have all the required documents, it’s time to decide whether you want to outsource production to other countries or manufacture the product domestically.
Domestic vs. Overseas Manufacturing
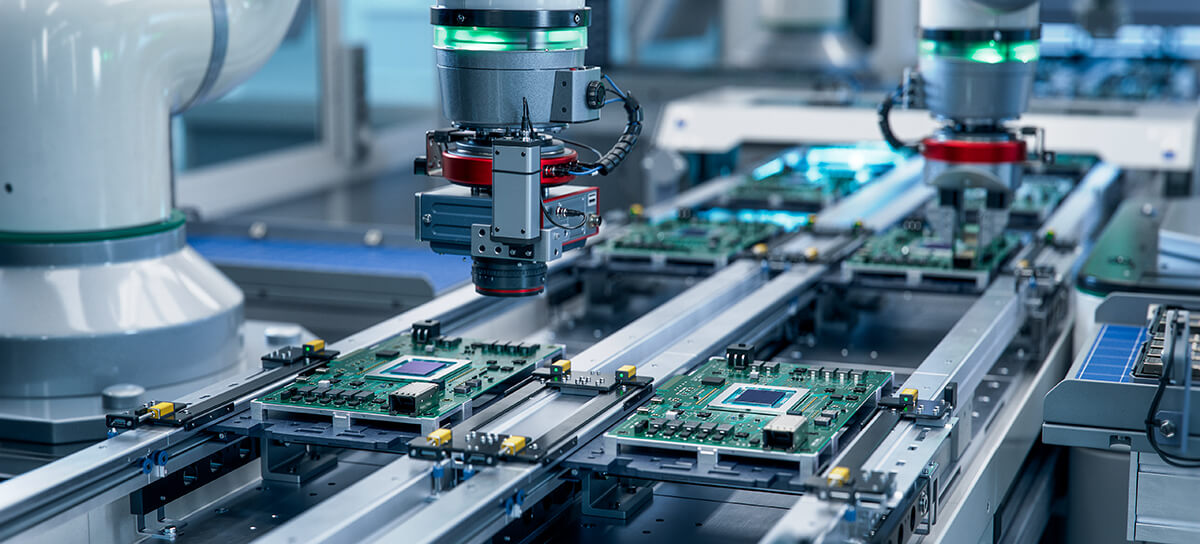
The Advantages of Domestic Production
1. No export and import taxes
When bringing goods to the domestic market from abroad, you will have to pay additional export and import duties unless there’s a special trade agreement between the two countries.
2. No shipping delays
When you think about the logistics of electronics manufacturing, domestic production looks more attractive. Transporting goods from other countries, especially those situated in distant regions, increases the risks of delay, lead times, and shipping costs. From this perspective, making goods domestically look more attractive.
3. Easier to solve issues and disputes
If a problem that requires your personal attendance occurs in the territory of your country, traveling there will take less time and effort than going abroad. Also, solving legal disputes inside your own country is easier than in international courts.
4. No communication barriers
Lastly, when dealing with people who speak the same language as you, there are fewer chances for misunderstandings and confusion.
The Advantages of Outsourcing to Other Countries
1. Reduced production costs
Third-country electronics assembly or manufacturing can be profitable due to lower costs of labor, raw materials, energy, and other indicators compared to developed countries in North America, Europe, and other regions. Additionally, one can benefit from various government incentives. The profit often outweighs additional taxes and shipping costs.
2. No capacity limit
By hiring a contract manufacturer in a country with an advanced electronics industry, you can benefit from its stronger capacity. That is if domestic manufacturers can’t offer the same scale of production. For example, it’s easier to find an EMS provider who will accept a large order in China than in Taiwan.
3. Bigger market
If you want to sell the products internationally, it is worth moving production to a larger potential market. This is one of the reasons many consumer electronics companies find China so attractive: its population is over 1.4 billion people.
4. Reputation
There are countries whose reputation in the electronics industry serves as a seal of excellence: for example, Taiwan, Japan, and South Korea. Some people are even willing to pay a bit more for the goods produced there. If your own country isn’t one of them, it may be worth outsourcing to such a destination.
Most Popular Countries for Outsourcing Electronics Production
When choosing where to outsource manufacturing, one should take into account several factors:
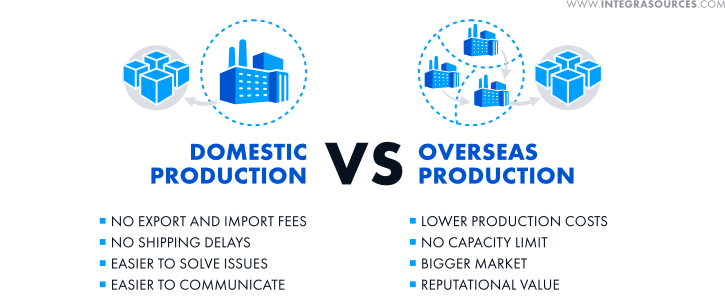
1. Labor costs and productivity
- Average factory and manufacturing salaries
- Labor productivity (GDP per hour worked)
2. Logistics infrastructure and transportation costs
- Logistics infrastructure development
- The cost of export-import operations
3. Macroeconomic and legal environment
- Macroeconomic environment rating
- Ease of doing business
4. The potential of the domestic market and export
- Imports of electronic components
- Export of electronic components
- Population size
Electronics can be outsourced to different countries located mostly in three regions: Asia, East Europe, and North America. Check our post Best Countries for Contract Electronics Manufacturing, Part 1 and Part 2 for more information on some of the countries in the list below.
Asia
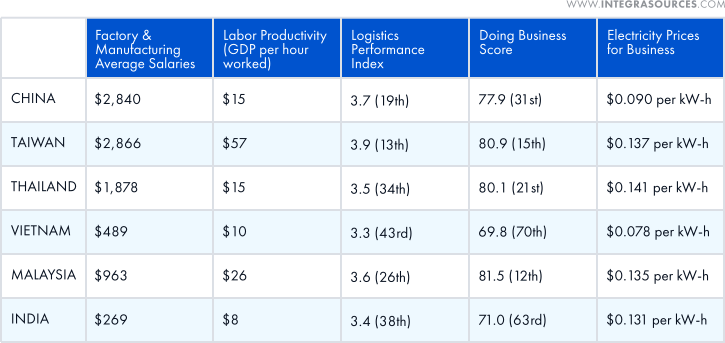
China’s electronics manufacturing is very strong. The country is the largest exporter of electronic devices not only in Asia but in the whole world due to various reasons: relatively low labor and energy costs, domestic suppliers of raw materials and components, advanced infrastructure, and factories with high output capacity.
At the same time, one should not forget about the trade war between China and the U.S., which makes importing goods to America from China more expensive due to high tariffs.
Another concern is potential IP infringement. If a product becomes popular, don’t be surprised to see a neighboring factory manufacturing something very similar. That’s why we recommend that you spend time developing protection against reverse engineering. One can also produce different parts of the device at different locations and assemble the product at yet another factory.
Taiwan started manufacturing electronics long before China. It can boast highly skilled specialists, high robot density, strong IP laws, and advanced infrastructure. The famous TSMC is located here. Such brands as Acer, Asus, and HTC come from Taiwan.
It is also worth mentioning Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, and India as these countries have low labor costs and are located close to China and Taiwan, the main manufacturers of electronic components. However, they lack skilled workers and developed infrastructure.
North America
The United States is considered one of the leading electronics manufacturers due to strong intellectual property protection, high quality, impressive labor productivity, and good public perception: around two-thirds of Americans prefer domestic goods over foreign products and are willing to pay 10% extra for them. However, the production cost here is much higher than in Asia.
Mexico, on the other hand, borders the U.S. and has much lower labor costs. It is regarded as a fast-growing electronics industry hub that produces ICs, computer memory and CPU chips, audio and video devices, and more. As a participant in the USMCA trade agreement, the country benefits from special duties for products exported to the United States. All this makes outsourcing production to Mexico potentially profitable if you target North America.
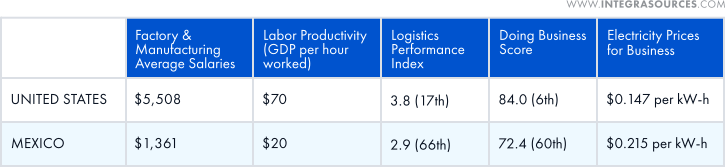
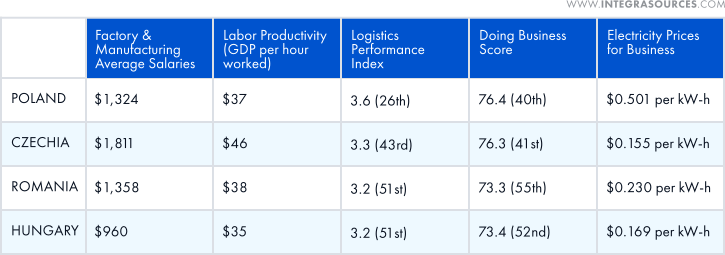
East Europe
Businesses targeting the European market may be interested in outsourcing production to Poland, the Czech Republic, Romania, and Hungary due to their proximity to Western Europe and lower production costs.
Your next task is to find a contract manufacturer.
What Companies Can Manufacture Electronics?
Electronics Manufacturers
There are several types of companies that specialize in manufacturing electronics. They are usually referred to as ODM, OEM, or EMS, which can be confusing. Let’s find out what these terms mean.
ODM stands for original design manufacturer. These are companies that both design and manufacture their own products, hold the intellectual property rights to the design, and sell the product to 3rd parties that, in turn, sell it under another brand. ODM businesses also allow their customers to make slight changes to the product, for example, change colors or packaging.
OEM stands for original equipment manufacturer. This term generally refers to businesses that produce parts or subsystems used in the final product sold by another company. It is a contract manufacturing model similar to ODM, except OEM businesses do not hold IP rights to the product design. Instead, they make products according to the specifications provided by the customer.
However, the term is ambiguous and can have other meanings. For example, it can refer to the manufacturers of systems that include other companies’ subsystems, which means they are brand owners. In this case, such companies as Apple, Microsoft, Samsung, or LG can be referred to as OEM companies.
Generally speaking, the type of company you are looking for is an EMS provider. You can also hear the terms CEM (contract electronics manufacturer) and ECM (electronics contract manufacturer), but they are basically synonymous with EMS.
EMS, or electronics manufacturing services, refers to a business model that implies not only contract manufacturing of electronic components and assemblies but also a range of other value-added services. Foxconn, the world’s largest contract manufacturer of electronics that makes products for Microsoft, Amazon, Sony, IBM, and other giants, is an EMS company.
The range of services EMS companies provide varies and can include any of the following:
- Electronics design
- Prototyping
- PCB assembly
- Electromechanical assembly
- Testing
- Aftermarket services
- Laser ID Marking on PCBs
- Conformal coating
- Return and repair services
- Supply chain management
Note that most manufacturers offer several types of partnerships instead of adhering to a single business model. So, one and the same company can be an original design manufacturer and offer contract manufacturing services at the same time. Examine the business’ website or contact its managers to make sure they offer the services you want.
Integra Sources specializes in electronics design and embedded software development. Although we do not offer manufacturing services, we have long-lasting relationships with several Chinese manufacturers whom we can recommend.
Enclosure Manufacturers
An electronic device or system usually consists of hardware (one or several printed circuit boards, LEDs, and other electronics) and an enclosure – a plastic or metal shell inside which the hardware is fixed. EMS providers usually specialize in PCB manufacturing, so you will probably have to order enclosures from another factory.
Some EMS providers do offer both of these services, but in most cases, they simply order enclosures from another facility located nearby. Such turnkey production is more expensive but makes managing the process much easier.
When contacting a factory, make sure to ask how many pieces of your device they can or are willing to manufacture, as some businesses may refuse to take your order.
What is Minimum Order Quantity?
Manufacturing an average printed circuit board can cost from $0.5 to $500, depending on different factors, including the board’s complexity. If we add the cost of enclosure manufacturing and assembly, the final cost of production of your device grows even more.
Generally speaking, larger order volumes come at lower prices, partially due to economies of scale and partially due to discounts that factories may offer in return for a big order. On the one hand, the more products you produce, the more you have to spend on warehouse rent. On the other hand, the profit from larger volumes often exceeds these extra costs.
However, some factories do not accept just any order as they require a minimum order quantity. MOQ is the lowest amount of products a contract manufacturer agrees to produce. To manufacture a product, a factory has to prepare a production line, buy and transport the required raw resources or assembly components, prepare a warehouse, etc. All this takes a lot of time and resources, so the order has to be large enough to spread out all the costs over all the manufactured units.
Manufacturers use two types of minimum order quantities:
Simple MOQs have only one requirement stated, either in the number of products to be produced or the cost of the order. If the contract manufacturer agrees to do the job only if you order at least 10,000 devices, that’s an example of a simple MOQ.
Complex MOQs have more than one requirement for orders. It could be the material or component type used, the minimum dollar amount, shipping costs, product color restrictions, or anything else they find critical to the profitability of their business.
The minimum order quantity depends on various factors including:
- Price of raw materials and components: businesses that supply factories with these resources insist on their own MOQs.
- The marginality of the product: the lower the margin, the more products factories have to manufacture in order to make enough profit.
- Market price: factories cannot set prices considerably higher than their competitors.
Small-size manufacturers usually offer low MOQs – starting at 25, 10, or even 1 pcs per order, which also makes them perfect for ordering prototypes during embedded hardware design. But there’s a limit to which they can scale their production. Large factories, on the other hand, can produce in huge quantities but usually insist on higher MOQs, starting at 500 or 1000 pcs per order.
You can learn about the MOQ of a particular EMS provider on their website. But remember that the minimum order quantity can be negotiated if you have something of value to offer in return.
Finishing Burst
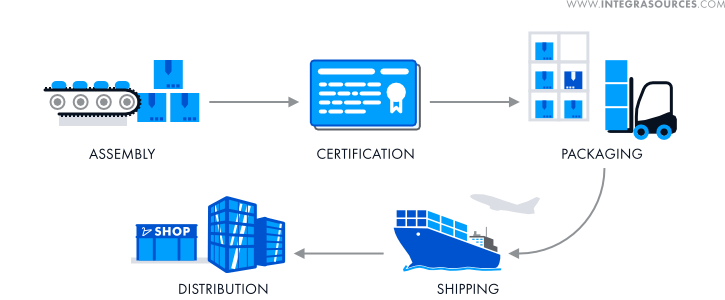
Product Assembly
After the electronics and enclosure for your product are manufactured, these components must be assembled. Assembly can usually be entrusted either to your EMS provider or to your enclosure manufacturer. Naturally, you will need to organize the shipping of enclosures or electronics to one or another unless you find a provider offering a turnkey service.
You can also assemble the final product in yet another location, even in another country. But it’ll complicate the logistics of electronics manufacturing even further.
It’s also a good idea to order a trial batch first. It will prove that the manufacturer can make a product of satisfying quality and that the production cost is low enough.
Testing & Certification
Before shipping a product to another country, you must obtain a certificate of conformity (CoC) or a letter of conformance. These documents certify that your product complies with specific quality and safety standards, laws, and regulations applied in the importing country.
The process of obtaining one varies depending on the type of product you’re importing and the country’s legislation. But there are general steps an importing company can follow:
- Identify the bodies responsible for issuing CoC.
- Contact them and request an application form.
- Fill out the form and provide supporting documents: the manufacturer’s contact information, copies of test reports, technical files, and manuals.
The authorized body will review the application and issue a CoC if everything is OK.
Packaging
Make sure to discuss packaging with the factory responsible for shipping your PCBAs or assembled products. During transportation, electronics can suffer from many hazards and, therefore, must be properly protected.
Bubble wrap or foam is commonly used for absorbing vibrations and impacts. To protect electronics and printed circuit boards from moisture, bags of silica gel are usually used. To shield electronics from electrostatic discharge events, one can use anti-static bubble wrap (it’s different from regular bubble wrap) or ESD bags (aka pink poly).

When hiring a forwarding agent, make sure the company has dealt with electronics and PCBAs before.
Shipping Products
Professionals spend years honing their skills in logistics, so here we can only give general tips.
When it comes to overseas trade, there are two common transportation methods: air freight and ocean freight.
Shipping goods by air is generally more expensive but takes less time. It suits small and light batches. Ocean freights take longer and are limited by sea ports only, but this is the cheapest shipping method.
When transporting goods by sea, you can choose between two shipment modes: FCL (full container load) and LCL (less than container load). In the case of FCL containerization, one container is filled with goods from one client. With LCL, a container is filled with goods from more than one client. LCL is generally cheaper for an average shipment but takes one or two weeks longer. Besides, the chance of damage, misplacement, and loss is higher. FCL is faster but pricier.

On land, shipping goods by rail is the cheapest option, especially when it comes to long distances. Trucks, on the other hand, usually move faster because they can choose shorter routes. But this speed difference only works for short distances.
Export/Import Customs Clearance
If you choose to manufacture and sell your product in different countries, you will have to deal with export and import procedures. Make sure you have prepared all the required certificates and permits.
The customs clearance procedure and the list of required documents depend on the local regulations, the type of product, and the trading agreements between the importing and exporting countries.
Export documents typically include the following:
- Export declaration
- Bill of lading
- Commercial invoice and packing list
- Certificates of origin for your goods
- Insurance documents
- Export license and permit (depends on the type of goods to be exported)
Import documents typically include:
- Import declaration
- Bill of lading
- Commercial invoice and packing list
- Copy of the import permit and/or license
- Certificate of origin
- Insurance documents
When a consignment arrives at the customs, the officers examine, classify, and evaluate it. Based on this evaluation and export/import tariffs, duties are calculated. Remember that the consignment cannot cross the border until the required duties are paid. Most countries have zero export duties for most goods except for agricultural products, natural resources, and semi-manufactured goods. The importer usually has to pay import duties and value-added tax. Forwarders and customs brokers/agents also charge a customs clearance fee.
To make things simpler, make sure you choose an experienced supplier that knows what documents you are going to need. We also recommend hiring a forwarder with expertise in exports from a particular country and knowledge of local procedures. Lastly, hire a customs broker as well so that the agency can handle the customs clearance process on your behalf. Most forwarders provide customs clearance brokerage as additional services.
Distribution
After the consignment arrives in the importing country, the products can go to wholesalers or distributors, who will distribute them to customers or retailers. If you produce the goods domestically, consignments can go to the intermediaries right from the factory. Details depend on your product type, business model, and other factors.
The easiest way to handle shipping is to hire a forwarding agent, whose responsibility is to arrange the transportation of goods from one location to another.
Conclusion
Outsourcing electronics production to foreign EMS providers complicates logistics and increases the product cost due to shipping costs and export/import duties – if you want to sell the goods in your own country. You will also face certain communication barriers and other issues.
Nevertheless, third-country electronics assembly or manufacturing can be very beneficial if it helps decrease production costs. Many Asian countries have lower wages and energy prices compared to the U.S., Japan, South Korea, and Western Europe. China’s electronics manufacturing industry is the largest in the world. Despite the growing labor costs and American sanctions, the country remains the world’s top location for contract electronics production due to the vast experience of local EMS providers, cheap raw materials, the proximity of component manufacturers, and advanced infrastructure.
If you don’t have a product design yet and want to turn your idea into a fully functional device, give us a call. Integra Sources has experience in developing consumer electronics, smart home systems, IoT devices, medical equipment, and other embedded solutions. We use the DFA/DFM approach in our work and always aim to minimize the manufacturing cost of products. We can also recommend reliable electronics manufacturers.
Share this article


Related
materials
Electronics Prototyping in Infographics
Any product development starts with designing a prototype. Although the first iterations are far from the final product, it’s an...
LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE
Manufacturing Electronics at Home vs. Outsourcing to Other Countries. Infographic
How can you prepare for mass production of your electronic device or system? What steps should you take? What are...
LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE

What Makes Electronics Prototyping so Important for Successful Product Development?
Electronics prototyping answers a range of crucial questions, such as how to solve a particular engineering problem, how to do...
LEARN MORE
LEARN MORE